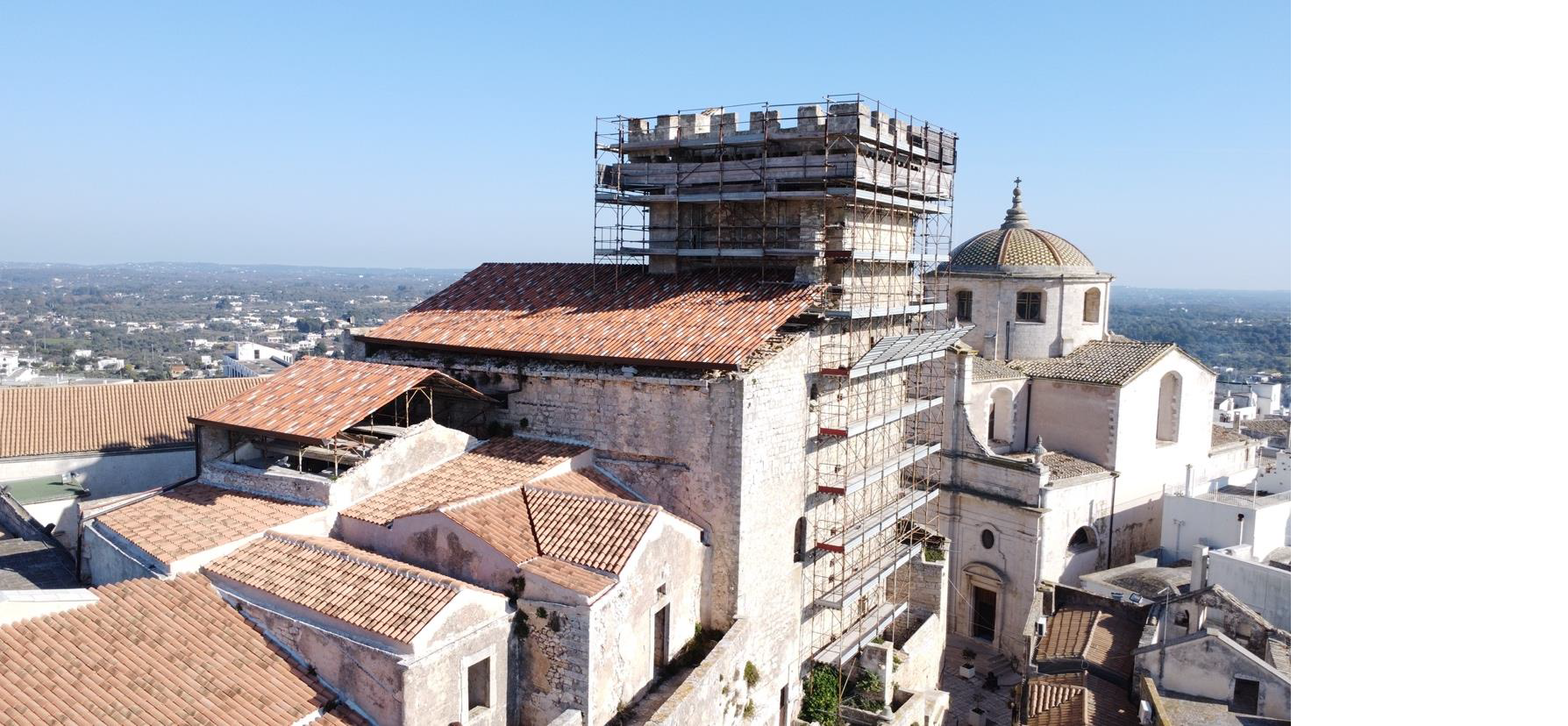
Inquadramento urbanistico
Il Palazzo Ducale è ubicato nel cuore della città di Ceglie Messapica (BR), ricade infatti in area A1 – Contesto Urbano Storico Medioevale del P.R.G. ricade altresì nelle aree “B. P.: Immobili e aree di notevole interesse” ed “U.C.P.: Città consolidata”, come da elaborato 6.3.1 del P.P.T.R.
The Ducal Palace is located in the heart of the city of Ceglie Messapica (BR), within the A1 – Historical Medieval Urban Context area of the Master Plan. It also falls within the areas “B. P.: Properties and areas of significant interest” and “U.C.P.: Consolidated City,” as per the document 6.3.1 of the Regional Territorial Planning Scheme (P.P.T.R.).
Inquadramento storico
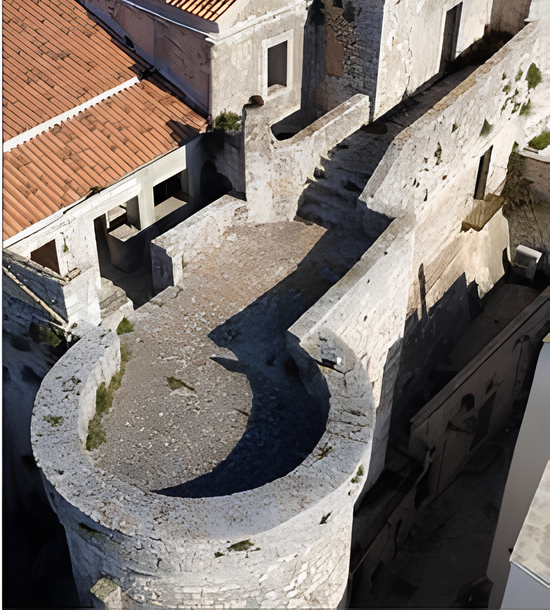

ll Castello Ducale di Ceglie Messapica, situato nel cuore della Valle d’Itria, è un edificio che ha subito diverse trasformazioni nel corso dei secoli. La sua origine risale al periodo normanno, con una struttura iniziale di torre difensiva, evolutasi poi nel tempo durante le epoche medievale e rinascimentale. Il castello subì modifiche sotto la dominazione sveva, con interventi che lo fortificarono ulteriormente, e successivamente, sotto i Sanseverino, che ne fecero una residenza sontuosa. Intorno al 1512, Aurelia Sanseverino e il marito Giovanni ampliarono e decorano l’edificio, attirando architetti e artisti di rilievo, rendendo il castello una dimora famosa anche alla corte del Regno.
The Ducal Castle of Ceglie Messapica, located in the heart of the Valle d’Itria, is a building that has undergone several transformations over the centuries. Its origins date back to the Norman period, with an initial defensive tower structure, which evolved over time during the medieval and Renaissance eras. The castle underwent modifications during the Swabian rule, with interventions that further fortified it, and later, under the Sanseverino family, it became an opulent residence. Around 1512, Aurelia Sanseverino and her husband Giovanni expanded and decorated the building, attracting prominent architects and artists, making the castle a famous residence even at the court of the Kingdom.
Nel corso del XVII secolo, sotto i Lubrano, il castello fu ristrutturato con interventi significativi, inclusa la costruzione di nuove sale e una scalinata imponente. Più tardi, nel XVIII secolo, il castello fu ulteriormente modificato, con la ristrutturazione degli interni e l’aggiunta di nuove strutture come una grande scuderia. Durante questo periodo, il castello era fortificato e custodito da una guarnigione, con un sistema di accesso complesso, che comprendeva un ponte levatoio, corridoi sotterranei e torri difensive.
In the 17th century, under the Lubrano family, the castle was restructured with significant interventions, including the construction of new rooms and an imposing staircase. Later, in the 18th century, the castle was further modified, with interior renovations and the addition of new structures, such as a large stable. During this period, the castle was fortified and guarded by a garrison, with a complex access system that included a drawbridge, underground corridors, and defensive towers.
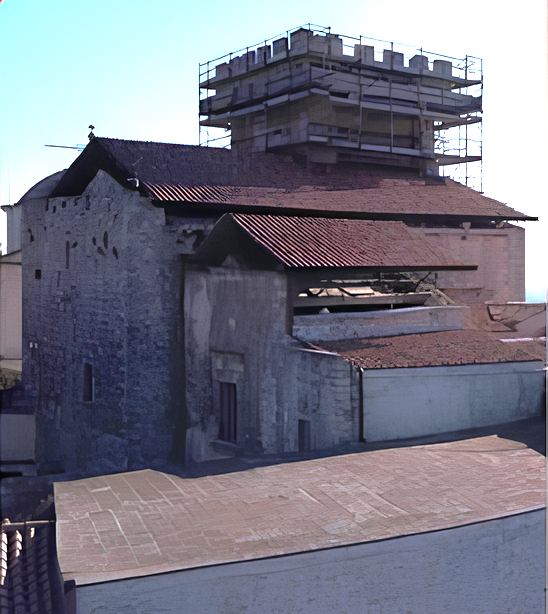

Nel XIX secolo, le modifiche furono più radicali: la famiglia Verusio, che aveva acquisito il castello, ampliò alcune stanze, distruggendo però alcune decorazioni originali. Furono poi costruite abitazioni nel fossato, trasformando parte del sito. Oggi, la famiglia Verusio, pur avendo perso il controllo diretto, rimane formalmente proprietaria di una parte significativa del castello.
In the 19th century, the changes became more radical: the Verusio family, who had acquired the castle, expanded some rooms but destroyed some original decorations. They also built houses in the moat, transforming part of the site. Today, the Verusio family, though no longer in direct control, still remains the formal owner of a significant portion of the castle.
